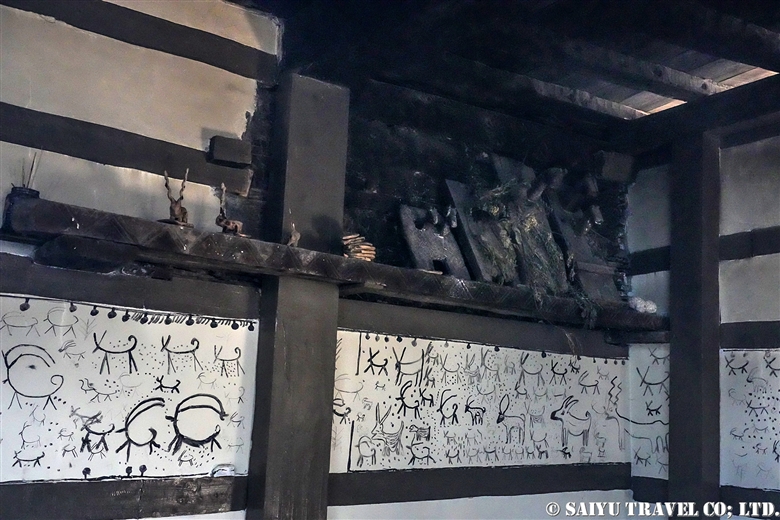
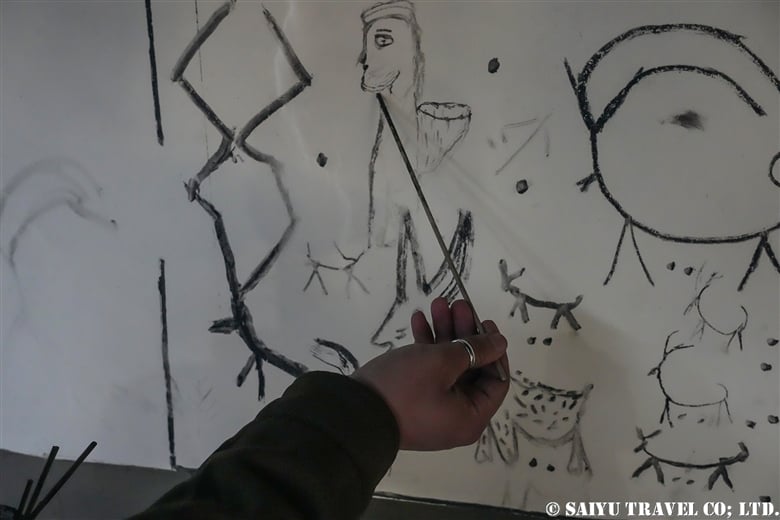
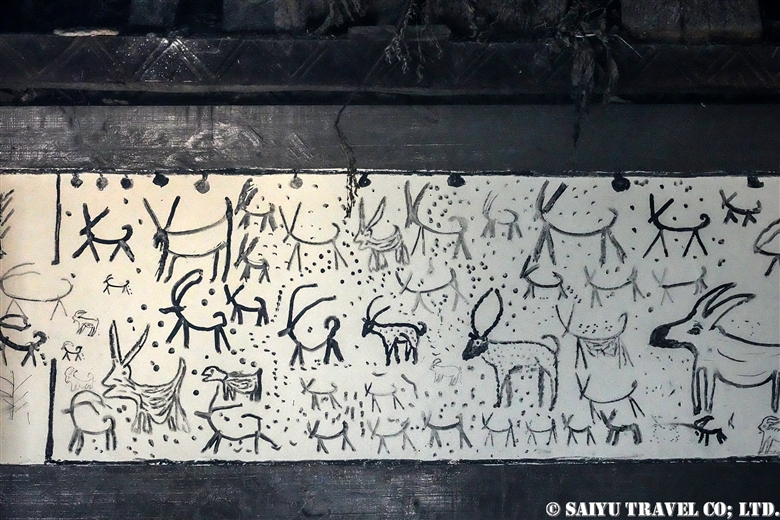
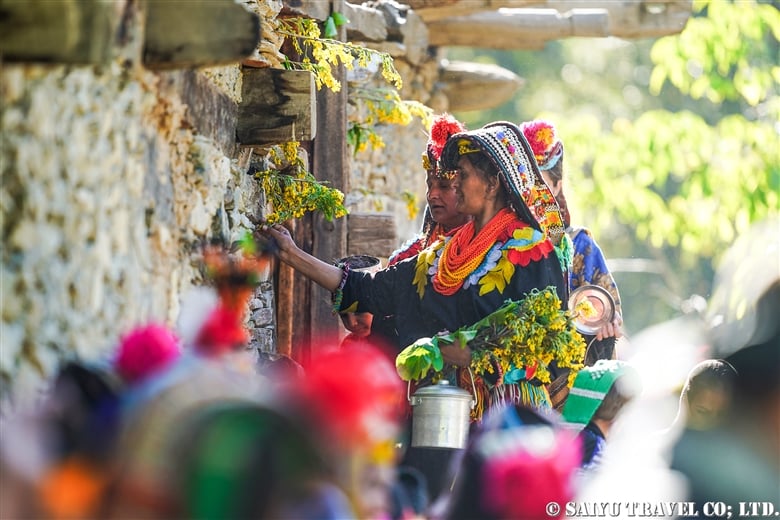
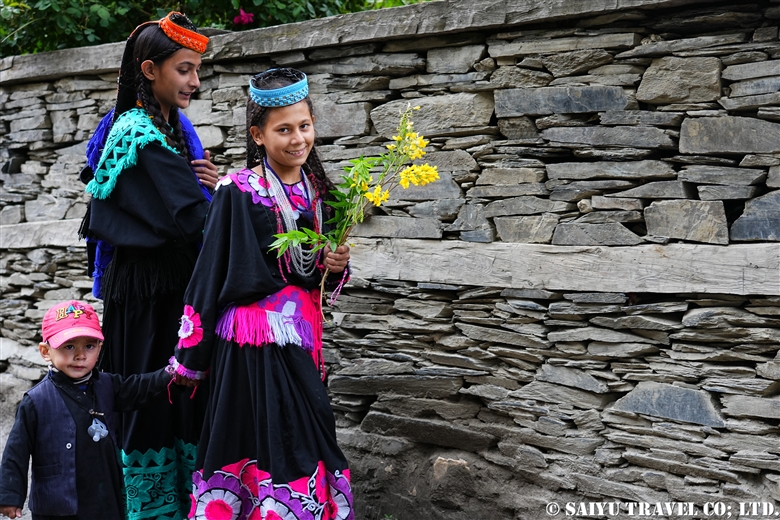
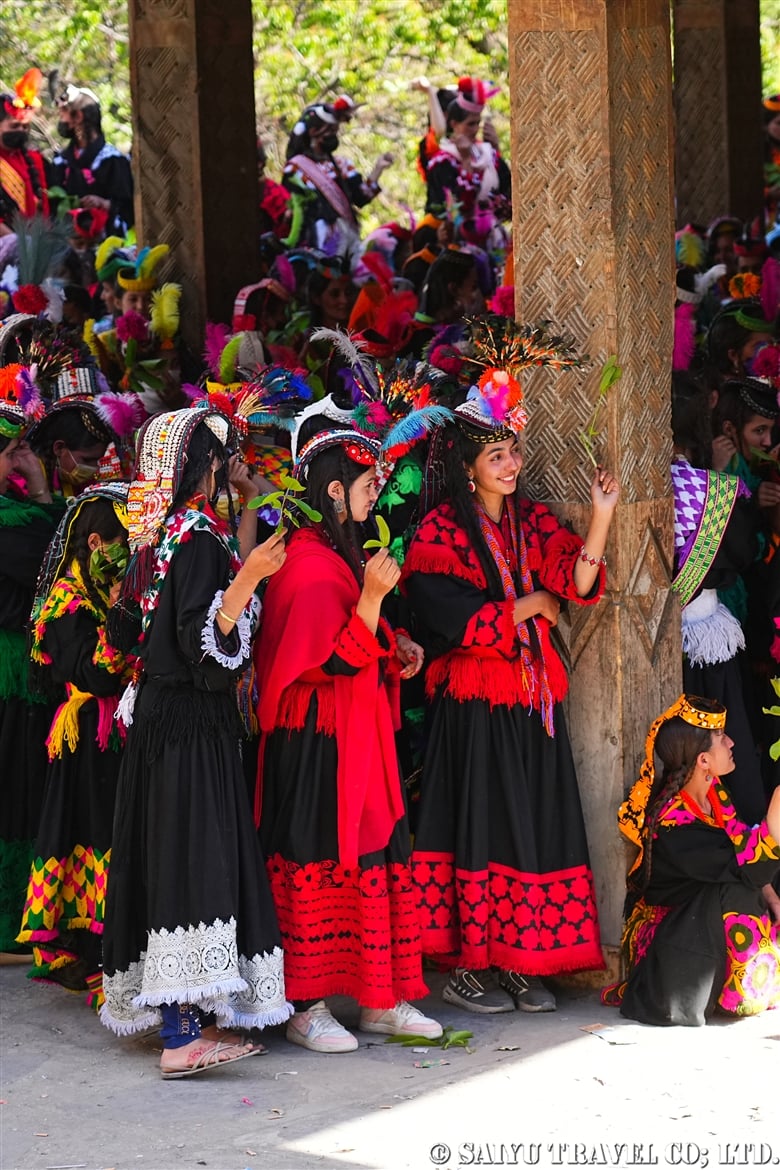
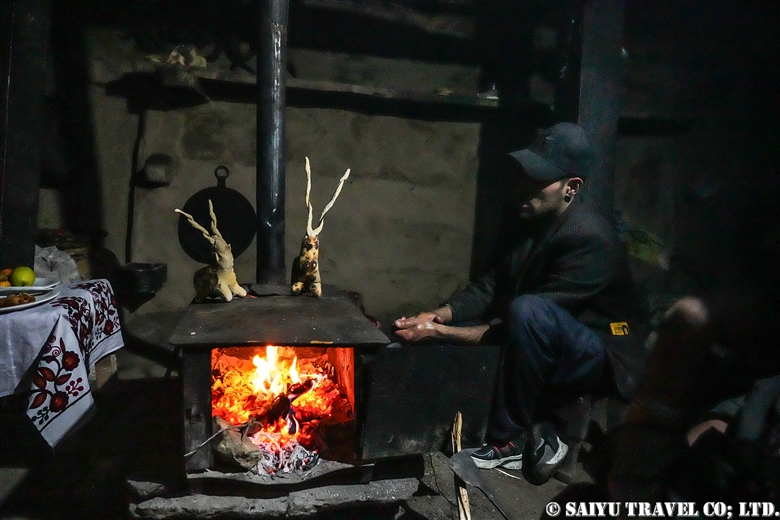The period of the Kalash Chawmos Festival known as “Ditch” is considered to be highly sacred. On the day of Pushao Adu, two sacrifices are performed: the first, called “Pushao Marat,” is a sacrifice to the gods done at Sajigor, and the second, “Istongas,” is a purification ritual for men. At the same time, a children’s rite of passage known as Goshnik is also performed.
At the guesthouse, the people were all abuzz with chatter. I heard them proclaiming that Balimain has arrived, and that the earthquake they’d had the previous night was actually the sound of Balimain’s arrival. They say that Balimain will stay to watch the sacrificial ceremony and the large bonfire at night, before moving on to the Bumburet Valley.
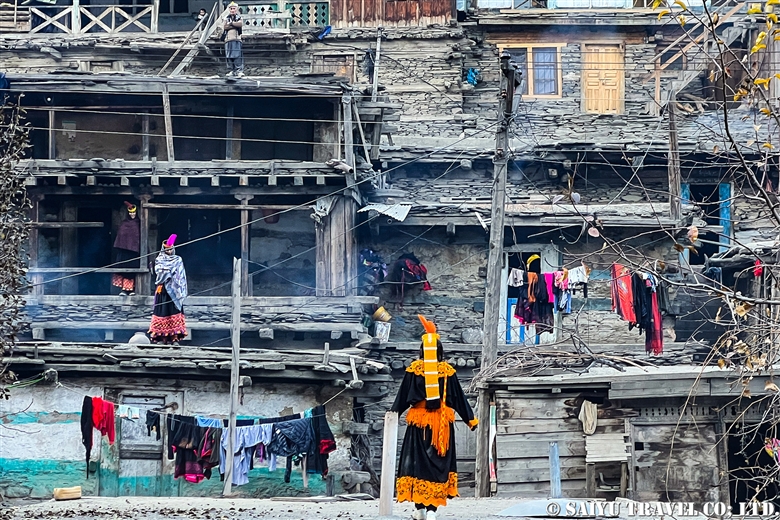
In the morning, all men in the valley wash their bodies and put on new clothes and shoes. The women wash all dishes and clean the house. After this, in addition to the existing rules about not touching Muslims, new rules are added until the sacred period is over. These rules state that no cleaning is to take place, that bread made before yesterday must not be eaten, and that bread must be made with new flour. Because of this, new dough was not available in time, so we had to have rice from Ayun for breakfast (which was very tasty).

Pushao Marat – Sacrifice to God
In the morning, the villagers gathered in the square to sing and dance, and at about 10:00 a.m., the large male goats selected from each family were taken to Sajigor. The men began to walk to Sajigor alongside the animals. Since women are not allowed to participate in the sacrificial ritual, this photo was taken by a Kalash man. While the ritual was happening, the women celebrated by singing and dancing.






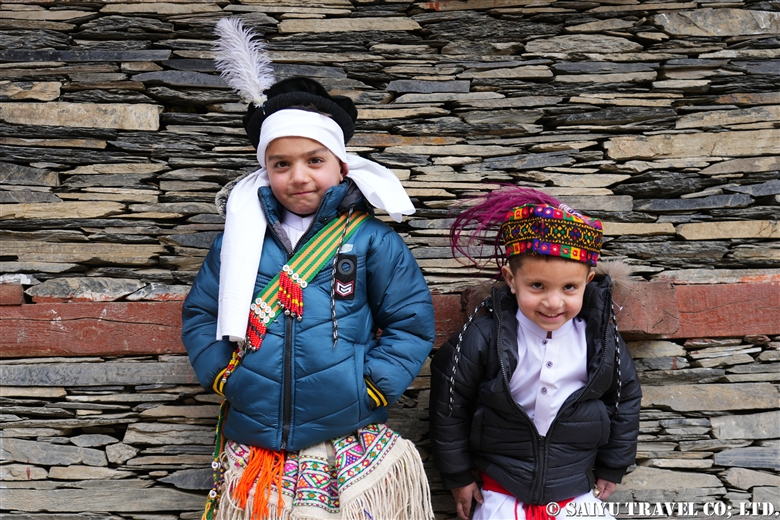
Goshnik – Rite of passage for children
Goshnik is a rite of passage for children, after which the boy or girl becomes a member of Kalash and observes its commandments. The parents of the child who is to receive the rite prepare fruits and gifts for the uncle who performs the rite. The uncle offers a male goat as a present. The relatives gather for the celebration, and the parents serve fruit and wine. I also saw visiting relatives give money to children undergoing this rite.





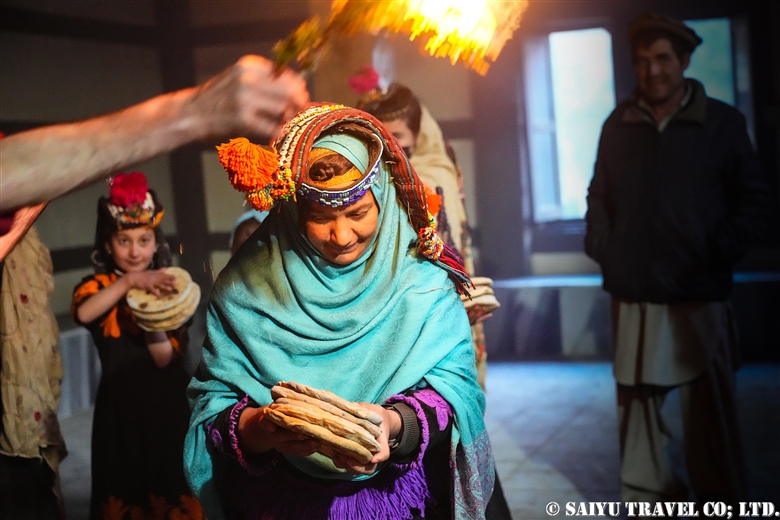
Purush Istongas – Sacrifices for the Purification of Men
Sacrifices are performed on the roof of the goat stable. The blood of the sacrifice is sprinkled on the faces of the lined-up men in a purification ritual. The Istongas ritual is held in the evening. This photo was taken by a Kalash man.
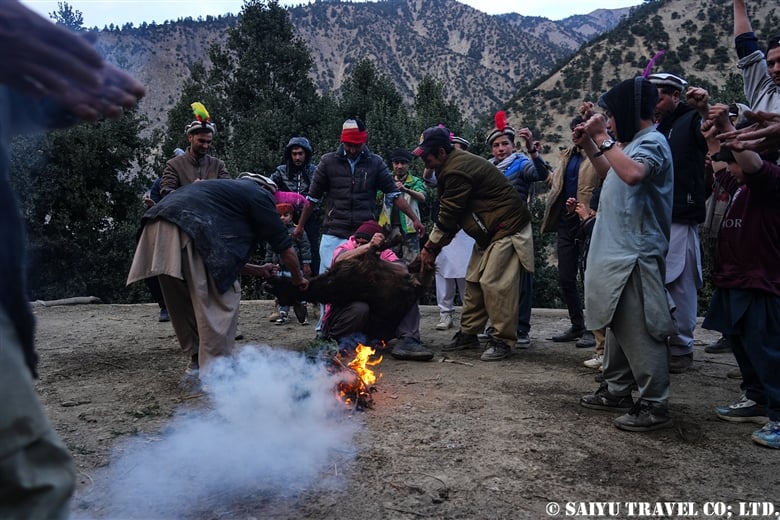
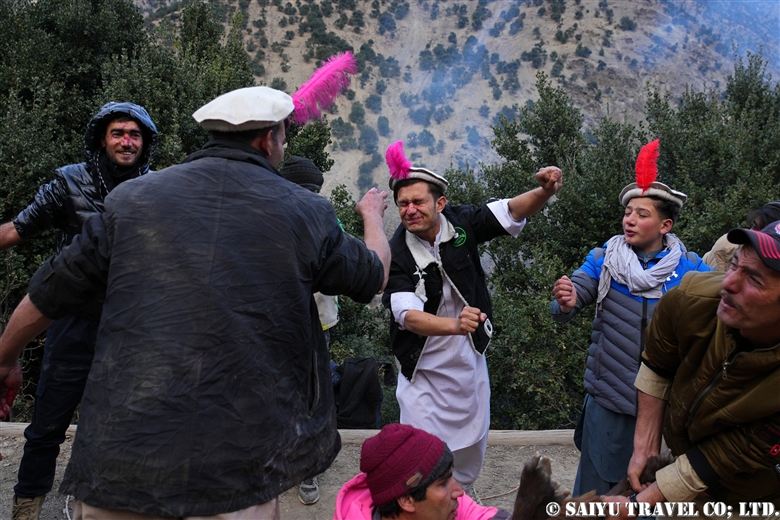
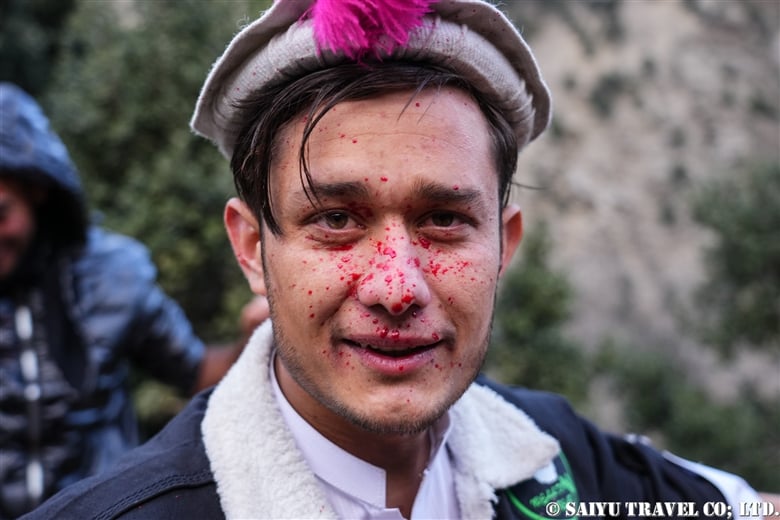



The sacrificial goat will be dismembered here and become the meat that is eaten during this sacred period. On this day, I learned a great deal about the beliefs and lifestyle of Kalash, a place where the ritual of sacrifice is still alive.
Text: Mariko SAWADA
Photo: Mariko SAWADA & Jamil
Visit: Dec 2024, Kalash Valley – Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
*The information presented here is based on interviews with people in the area. Please note that the descriptions and explanations of the rituals may differ depending on the source.
*Chawmos Festival – Kutram: The Kalash Rituals Still Alive to This Day
*Chawmos Festival – Shishao Adu: The Kalash Rituals Still Alive to This Day
*The Joshi Spring Festival: A Kalash Ritual
*Contact us, Indus Caravan for more information or to make arrangements for visiting Kalash valley.
*Please follow us on Youtube, Instagram & Facebook
Category : - Kalash Valley > ◆Khyber PakhtunkhwaTag : Bumburet Village , Shishao Suchek , Khyber Pakhtunkhwa , Pakistan Travel company , Pushao Adu , Pakistan Blog , Pakistan tour operator , Pushao Adua , Pakistan Travel Blog , Pakistan Photography Tour , Rumbur , Bumburet , Bumburet valley , Ayun , Indus Caravan , Rumbur valley , Chitral , Chawmos , Kafiristan , PakistanBlog , Chaumos , Kalash , Kalasha Valleys , Chawmos festival , Kalash valley , Bomboret village , Shishao , Kalasha