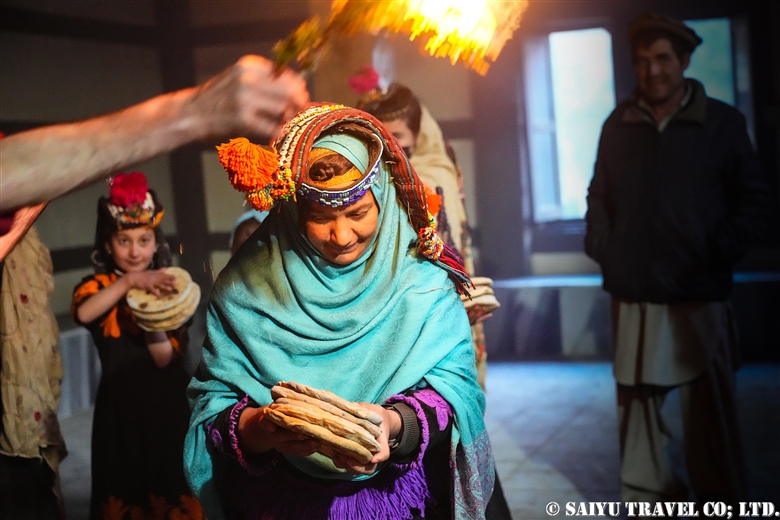
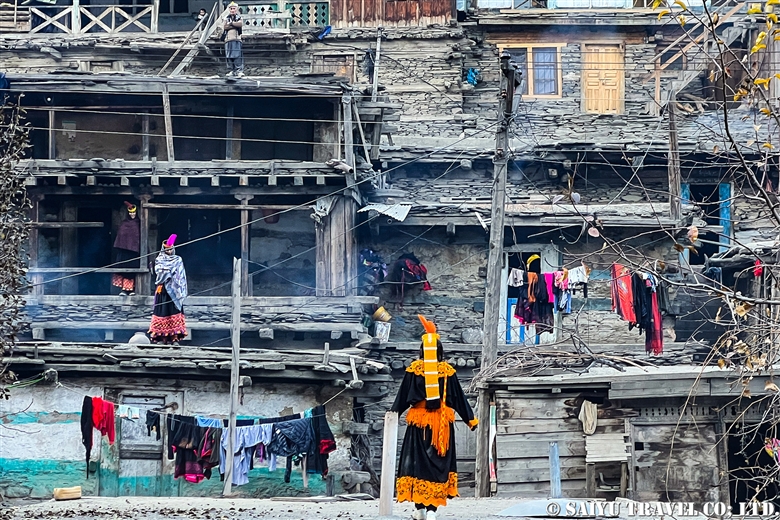
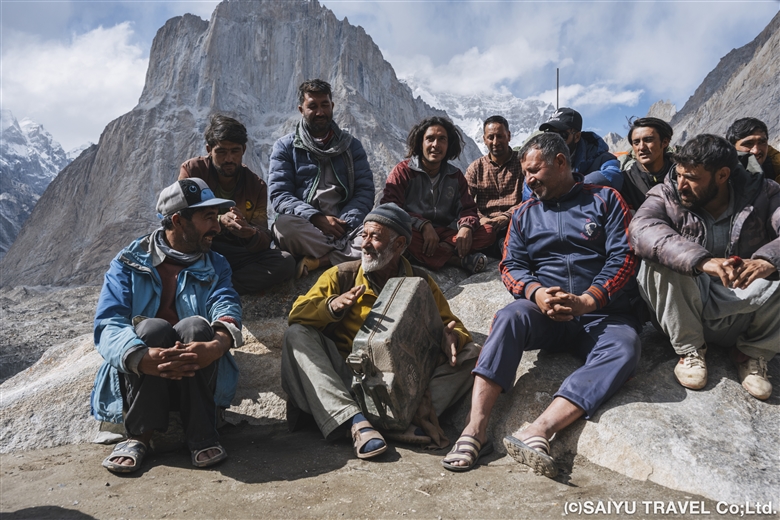
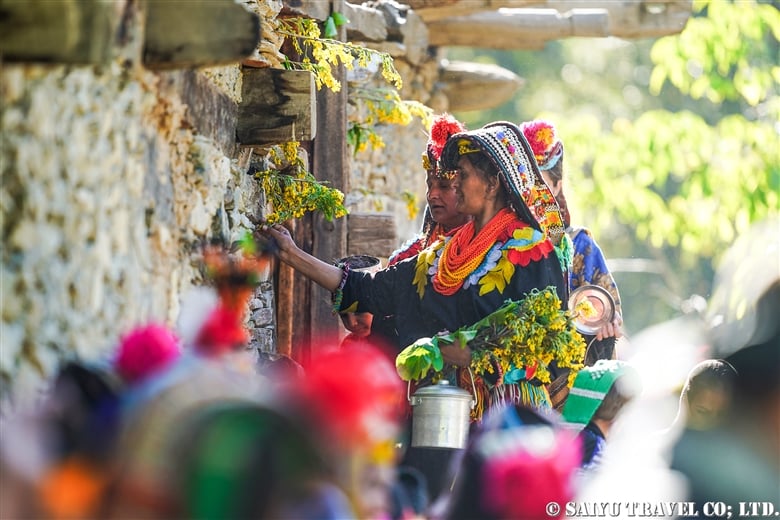
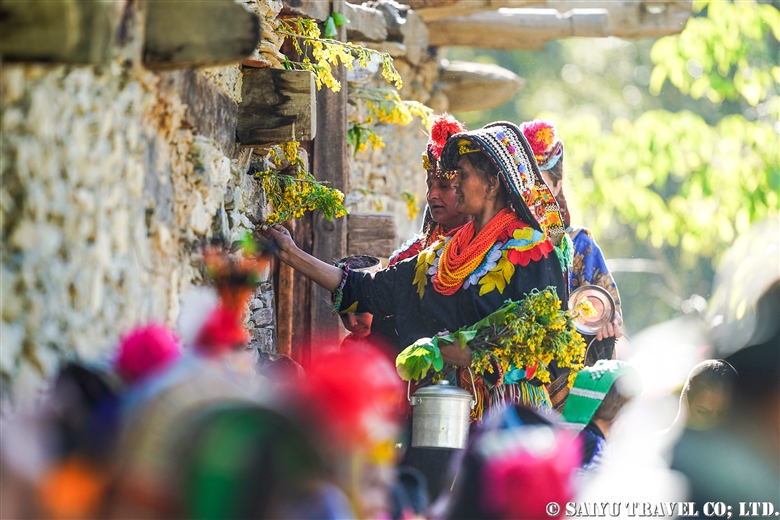
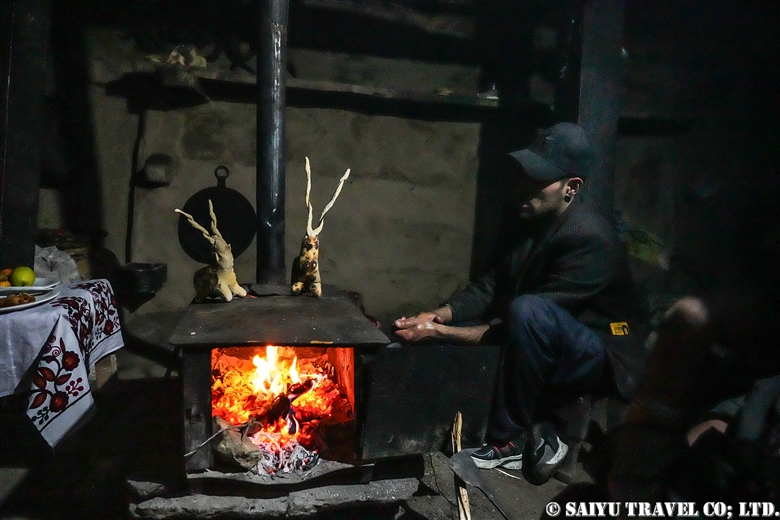The ceremony to welcome the god Balimain of Kalash had finally begun. The following is a report on the women’s purification day known as “Shishao Adu.”
The day before Shishao Adu is a day for preparing the stone slab with which the Shishao, the bread for the women’s purification ceremony, will be made. The men go into the mountains to look for suitable stone slabs and leave them in a safe place, so that the women don’t touch them until they are ready to use. Meanwhile, the women prepare the flour used to make Shishao.


On the morning of Shishao Adu, women gather on the riverbank to prepare for the purification. They bathe in the hut and wash their hair. After this, they cannot bathe until the sacred period is over.

Shishao Adu is a day of purification for women. After this day, no newcomers are allowed to enter the Rumbur Valley. No exception is made for foreigners, nor for Muslims living in the valley—they are likewise not allowed to enter the village of Kalash. The female Kalash relatives who come from Bumburet to celebrate the children’s rite of passage known as “Goshnik” must also undergo this purification. We foreigners were also purified. When I walked around the village, people asked me if I had showered, and if I was wearing new clothes. They believe that if anyone who does not follow the regulations of the Kalash religion is in the valley, it will bring them misfortune.

Shishao making begins at the Temple.

A man kneads purified dough to be used for the making of Shishao. The men’s hands are purified, and they are not allowed to touch anything other than the ingredients for Shishao—including themselves.

Using stone slabs and stones from the mountains, the men crush the walnuts which will act as filling for the bread.

Men are required to bake five Shishao for each female member of the family, and in families with many female members, baking Shishao can start even in the early morning.
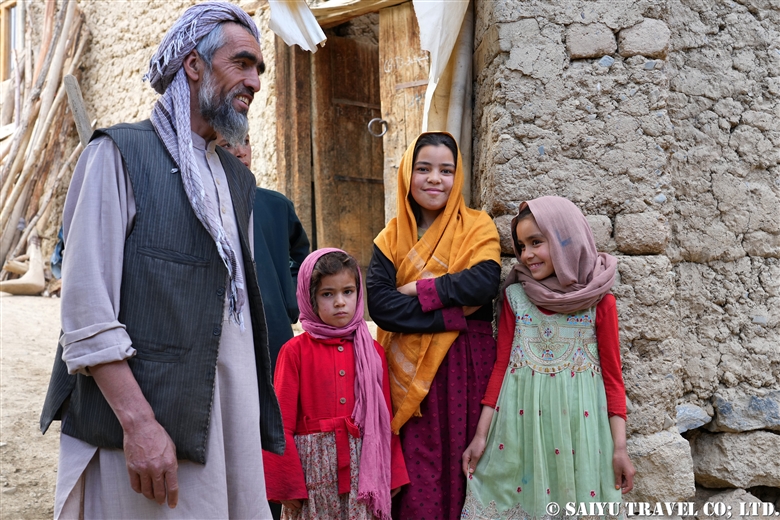
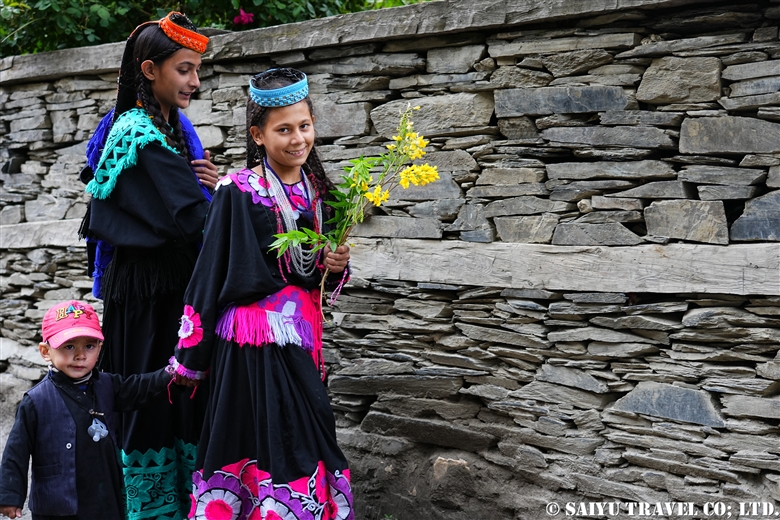
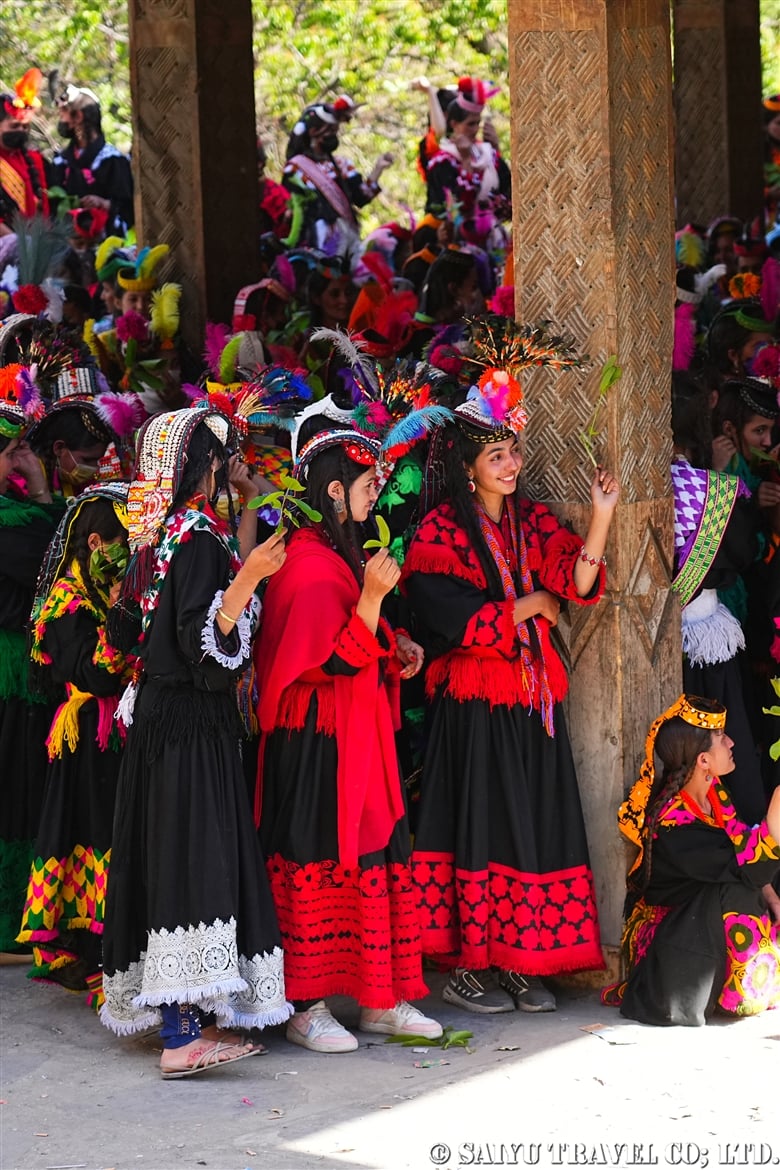
The women’s purification ritual, Shishao Suchek, had begun. The women prepared new clothes, and some of the girls were dressed up almost as much as they are during the spring Joshi festival.




A woman with a very innovative headdress. She said her mother made it for her.

A traditional-style headdress known as a Kupas. Its colors are very modern. The traditional materials and colors that are typically shown in books are nowhere to be seen these days. It seems that Kalash women are always chasing the latest fashions.
The Shishao Suchek ritual at Temple Jestak Han had finally begun. Notably, it can also take place outside, in the open air.



After this purification, the woman must remain pure for seven days. This involves a serious of strict rules, such as not touching Muslims, not eating chicken, eggs, cow’s milk & dairy products, honey, and so on.
Getting the opportunity to see these people live their lives and practice their faith was truly a beautiful sight.
Text & Photo: Mariko SAWADA
Visit: Dec 2024, Kalash Valley – Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
*The information presented here is based on interviews with people in the area. Please note that the descriptions and explanations of the rituals may differ depending on the source.
*Chawmos Festival – Kutram: The Kalash Rituals Still Alive to This Day
*The Joshi Spring Festival: A Kalash Ritual
*Contact us, Indus Caravan for more information or to make arrangements for visiting Kalash valley.
*Please follow us on Youtube, Instagram & Facebook
Category : - Kalash Valley > ◆Khyber PakhtunkhwaTag : Pakistan Travels , Shisao Adu , Pakistan Blog , Pakistan Travel company , Shishao Suchek , Pakistan Travel Blog , Pakistan tour operator , Rumbur , Pakistan Photography Tour , Bumburet , Ayun , Indus Caravan , Bumburet valley , Chitral , Rumbur valley , Kafiristan , PakistanBlog , Chawmos , Kalash , Kalasha Valleys , Chaumos , Kalash valley , Bomboret village , Chawmos festival , Kalasha , Bumburet Village , Shishao , Khyber Pakhtunkhwa